Discovering unforeseen challenges and driving breakthroughs – this is the essence of the WASP Research Arena for Robotics (WARA Robotics). We are creating a tangible, industry-relevant environment tailor-made for revolutionary industrial automation research.
Objective of WARA Robotics
WARA Robotics was created to explore technologies in their relevant environments, which allows researchers to discover and explore unexpected challenges otherwise invisible.
Three Main Tasks
WARA Robotics is designed to support research connected to common industrial tasks: kitting, assembly, and lab automation. Kitting is the process in which all material needed for assembling a product is collected and delivered to a workstation. This task requires refined navigation and manipulation skills such as pick and place, as well as perception and object detection capabilities. Assembly is the task performed when the pieces are put together. This additionally demands contact-rich manipulation where the contact dynamics reflecting the physical properties of the pieces exhibit a high degree of variation. Lab automation is the process of integration of new technologies to improve or produce new processes in medical, chemical and analysis labs, among others.
Meet Our Robots in the Video
The three tasks exhibit a wide range of research challenges crucial for further developing flexible automation. Robots not only have to operate in complex environments, but they also need to collaborate with their human counterparts safely and effectively. See the following video for some examples.
Resources and Partners
The WARA Robotics group currently has ABB, Ericsson, and Algoryx as industrial partners, as well as researchers engaged from most of the WASP affiliated universities, with the ambition to add more companies and universities in the future.
In WARA Robotics, our activities are focused around the two environments that we offer, equipped for industrial automation research: a physical testbed at ABB Västerås, as well as a digital counterpart for simulation, which can serve as a digital twin for most applications.
Physical Lab
The Physical Lab is located in ABB Corporate Research Center (CRC) in Västerås (Forskargränd 7, 722 26). As shown in Figure 1 and 2, it consists of an open space layout to enable experimentation with mobile robots.
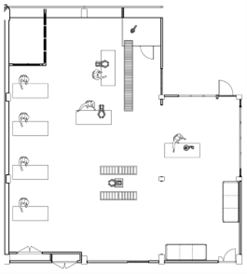
Figure 1. Layout of the physical lab in Västerås.

Figure 2. Photo from inside the lab where different elements are shown.
There are three types of robots in the lab (see Figure 3):
1. Collaborative robots
- Collaborative robots are industrial robots that are designed to safely operate with humans. In the lab, we have IRB 14000 (also known as YuMi) and CRB 15000 (also known as GoFa) robots
2. Industrial robots
- Industrial robot arms are robot systems used in manufacturing and other automated tasks. The main difference with collaborative robots is that by design they are not required to have as many safety features, which constrains them to being installed in human-free spaces. In the lab, we have an IRB 1200.
3. Research platform
- ABB CRC in Västerås has developed a research platform based on the YuMi dual robot arm combined with a mobile base. mYuMi is not a commercial product, but it has been made available for use in WARA Robotics.

Figure 3. Three different types of robots are available in the physical lab in Västerås.
Digital Lab
The physical lab has a simulated counterpart, where users can develop and test applications during their research (see Figure 4 and 5). In the digital lab, the robots and environment from the physical lab are made available in a simulated setup, which preserves the same interfaces. This allows achieving seamless integration between the physical and simulated robots. There are two versions of the digital lab:
1. Gazebo
- A popular open-source simulator in robotics with a plethora of control and sensor plugins that, when combined with ROS 2, formulates a complete R&D platform with easy access to state-of-the-art algorithms.
2. AGX Dynamics – Unreal Engine
- Algoryx, together with ABB, has developed a high-fidelity simulation model of the mobile lab environment and mYuMi. This model has state-of-art graphics, an ABB virtual controller for the robot, and allows high-fidelity physical interaction between the robot and its environment.
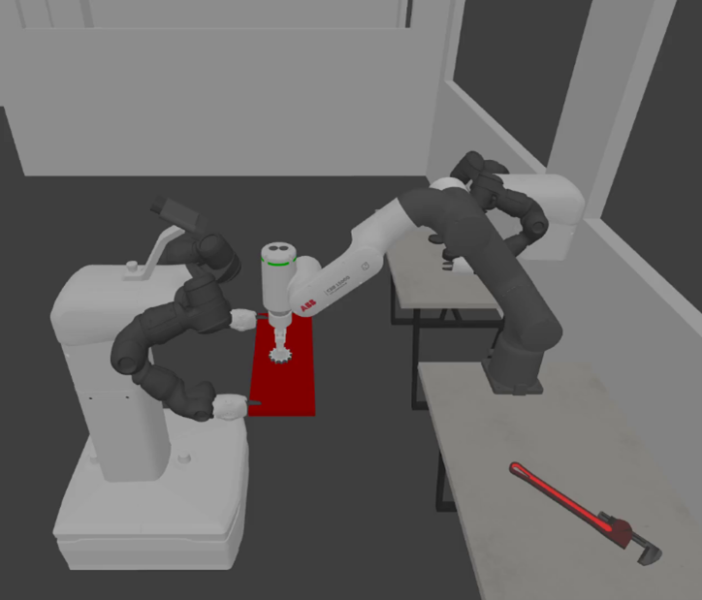

Figure 4. Gazebo-based simulation.
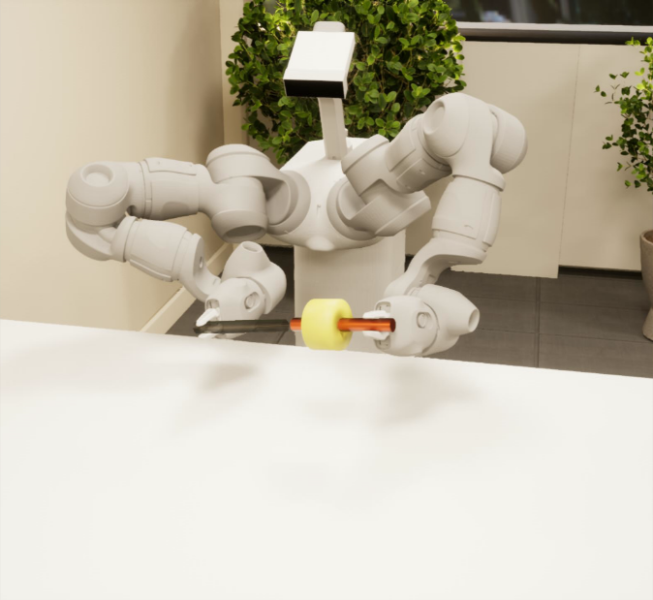

Figure 5. Simulated environment developed by Algoryx.
Interfaces
The robots in the lab support the following interfaces for communication and programming:
- RAPID: programming language for ABB robots
- Robot Web Services (RWS): RESTful API for communication with ABB robots
- Externally Guided Motion (EGM): remote control interfaces for movement control of ABB robots
- ROS 2 Humble
- Python: through RWS Python wrapper (compatible with RWS 1.0 & 2.0)
Integrating with robots is usually a time-consuming task in robotics research. For this reason, we have developed ROS 2 drivers for the robots in the lab, to ease integration and add flexibility when switching among different robots. However, we are more than happy to expand the listed interfaces to better accommodate different integration needs.
Support for Research Activities
WARA Robotics goal is to support research in several areas, some of which are:
Reinforcement Learning
- Reduction of samples
- Sim-to-real transfer
- Multiple robot data generation
Automated Reasoning
- Task planning
- Resource scheduling
- Motion planning
- Multi-robot coordination
Perception
- Segmentation and scene understaning
- Object recognition and trackning
- Multi-modal perception
Human-Robot Interaction
- Multi-modal interaction
- Learning from demonstration and observation
Assembly with Dual-arm Robots
- Utilization of dual arms in assembly
WARA Robotics Community
As the community grows, we look forward to expanding this list. If the research you are conducting is not listed, please reach out to us anyway and we can discuss if it is possible to include.
We welcome all academic and industrial researchers and PhD students in Sweden to contact us if they have any questions. Be part of the WARA Robotics community!


