Generative AI to ensure secure operation in dynamic edge scenarios
In the future, computing and communication systems must accommodate a diverse range of applications, including telemedicine, intelligent transportation, extended reality (XR), and personal assistants. Some of these are already a reality, thanks to powerful computer hardware, faster and more reliable mobile communication (such as 5G), and significant advancements in AI and software technologies. Notably, generative AI has made remarkable progress in recent years, unlocking numerous possibilities for research in this field.
This project aims to leverage generative AI to address critical challenges related to secure resource allocation in dynamic edge scenarios. Researchers will explore how to specify, train, and verify generative AI models for creating orchestration mechanisms and protocols. Their goals include detecting and mitigating attacks against intelligent Function as a Service (FaaS) systems and enabling runtime security verification for both manually and automatically generated orchestration mechanisms.
Long term impact
The project will give scientific impact by addressing hard security problem, presenting the results at high impact conferences and publishing in high impact journals. It will give societal impact by addressing important research problems essential to secure future telecommunication infrastructures. Finally, Industrial impact is provided through direct collaboration with large Swedish industries and through transfer of graduated PhDs and with master thesis projects.
None of the currently available FaaS platforms, such as AWS Lambda, Azure and Google Cloud, Apache OpenWhisk and IBM Cloud offers full support for service level objectives such as latency requirements and they cannot give the wanted reliability guarantees. Relative few works address the security of FaaS orchestration as such. Most prior work has been focused on increasing the integrity and confidentiality of the functions. The project proposes to use generative AI technologies to tackle some of the key challenges of secure resource allocation in dynamic edge scenarios.
Designing resilient systems is known to be very hard and time consuming. Consequently it is not enough to work with manually crafted designs, but the possibilities using generative methods must also be utilized. This is a new and very promising area where SOURCE will contribute with a unique line of research from Swedish and international perspectives.
The security problems in future autonomous systems are closely connected to learning techniques and cross-fertilization between cyber security expertise and AI expertise is needed to tackle the problems at hand. The SOURCE project creates the foundation for such new collaborations. Furthermore, the project addresses key technology areas for next generation computing and telecommunication infrastructures.
The project team consists of a chosen mixture of senior researchers in the fields of cyber security and AI.
PI C. Gehrmann has been working with security for connected systems for more than 25 years, in academia and industry as well as for spin-offs.
The co-PI M. Asplund has extensive experience in formal analysis and security mechanisms for cyber-physical systems.
Co-PI F. Heintz has two decades of experience in the SOURCE application area, unmanned aerial vehicles, besides being a leading researcher in AI.
Co-PI A. Aminifar bridges the areas of machine learning and security and has been working with both security and machine/federated learning.
Scientific presentation
Background
The telecom industry is in an accelerated transition towards distributed cloud computing where computations are pushed closer to the devices at the edges of the networks. At the same time, we see a rapid increase in new threats against vital applications and system functions depending on the new communication infrastructures. To address these new threats, considerable new research efforts are required. Especially, new technologies which both utilize and protect against the new possibilities provided by artificial intelligence (AI) are needed.
Purpose
This cross-disciplinary project focuses on securing resource allocation in dynamic edge scenarios. The aim is to investigate how to specify, train and verify generative AI models for creating orchestration mechanisms and protocols, to detect and mitigate attacks against intelligent FaaS systems, and enable runtime security verification of both manually and automatically generated orchestration mechanisms.
Methods and approach
The SOURCE project investigates secure orchestration principles, using generative AI methods for resource protocol design including automatic verification of the designs. New models and principles will be verified performing experimental research with open data. The project will be working with state-of-the-art dynamic resource allocation techniques as well as Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs). In particular, the project will be based on the WebAssembly (Wasm) technology for distributed computing. Intel TDX and AMD SEV will be the technologies for experimental evaluations of protocols for the verification of TEE resources. SOURCE collaborates and contributes to theWARA-Ops regarding collection of distributed computing log data and for anomaly detection. It also collaborates with the WARA-PS to test the new concepts and principles on drone systems in a dedicated scenario based on a Gränsö rescue mission.
Figure 1 give an overview of the scenario the project addresses and the figure depict the main functions in the system which the project will directly address. The focus is on general applicable principles and methods and the results will be evaluated on data from real and simulated systems.
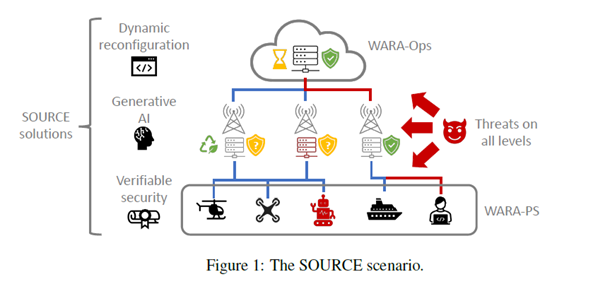
The project is divided into four different work packages, which relate to and complement each other.
WP1: Attack Detection and Prevention in Dynamic Resource Allocation Systems. Even if anomaly detection, in general, has a long research tradition, detection and mitigation of attacks against intelligent FaaS systems is a new and emerging research field. In this work package, the group will address the research problem, leveraging on their previous work on secure resource allocation, including in the context of clouds and UAVs.
WP2: Generative AI Methods for Dynamic Resource Allocation. Generative approaches such as Large Language Models (LLMs) have successfully been used to generate agent behaviours in virtual environments. In this work package, the project group will apply these techniques to generate unique protocols for workload orchestration. By generating the protocols, potentially constrained to counter particular attacks or have certain properties, the expectation is to significantly increase the security of the orchestration.
WP3: Verifiable Security for Automatic Workload Orchestration. With new models for resource allocation in the edge-cloud continuum, possibly created using generative adversarial learning models explored in WP2, there is an increased need to establish provably secure resource allocation mechanisms. In this work package the project group designs novel methods to enable resource allocation and orchestration for use-cases with high requirements on security assurance. They utilize two main security mechanisms: remote attestation and online protocol verification.
WP4: Demonstrator. WP4 will develop a demonstrator system based on an extended rescue mission scenario formulated in collaboration with WARA-PS. This involves drone image processing and dynamic resource allocation in the presence of potentially adversarial actors where groups of drones need to allocate image processing task to nearby Edge resources.


